Intercommunal violence, terrorist attacks fuel tensions in W. Africa
Inter-communal violence and persistent attacks by extremists, continue to undermine peace and security across West Africa.
The UN’s top official in the region warned the Security Council on Thursday, while calling for sustained engagement with all partners to urgently advance a holistic approach to peace.
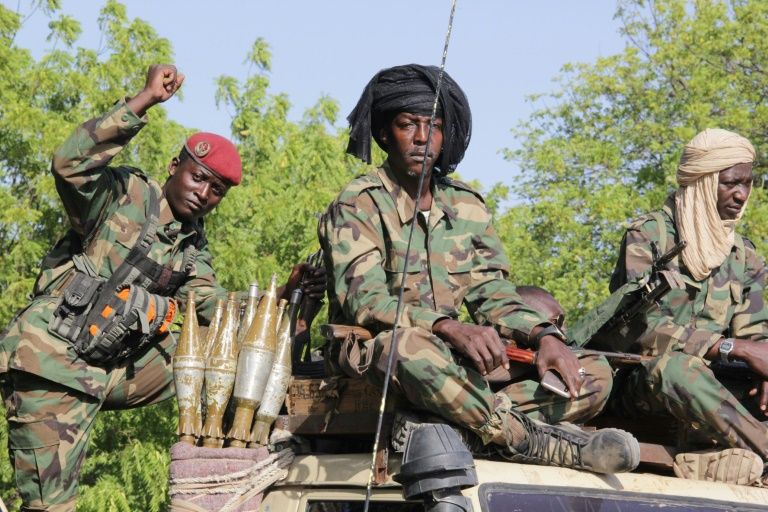
Mohammed Ibn Chambas, Special Representative of the Secretary-General and Head of the UN Office for West Africa and the Sahel (UNOWAS), said that despite “intense and sustained” efforts by concerned countries, violent extremists continue to attack security forces and civilians alike, with children recruited into fighting in Burkina Faso, Mali, Niger and Nigeria.
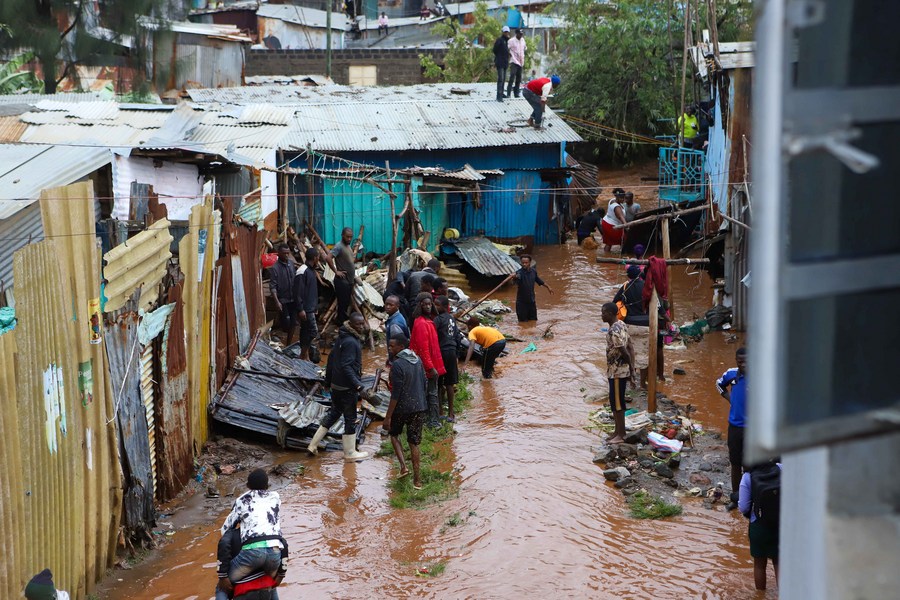
Presenting his latest report, the UNOWAS chief described security conditions as “extremely volatile”. In Burkina Faso alone, as of June, 921,000 people have been forced to flee, representing a 92 per cent rise over 2019 figures.
In Mali, nearly 240,000 people are internally displaced, 54 per cent them women, while in Niger, 489,000 people were forced to flee.
This includes internally displaced persons, Nigerian and Malian refugees. In Nigeria, 7.7 million people will need emergency assistance in 2020.
As national and multinational forces intensify counter-terrorism operations, some communities have organized volunteer groups and self-defence militias for protection.
Human rights groups have raised concerns over alleged abuses by these militias, as well as by security and defence forces.
“The growing linkages between terrorism, organized crime and inter-communal violence cannot be overemphasized”, he said. “Terrorists continue to exploit latent ethnic animosities and the absence of the State in peripheral areas to advance their agenda.”
He urged the United Nations to remain committed to working with all partners, building national and institutional capacity, improving community resilience, and advocating for good governance, political inclusion, respect for human rights and adherence to the rule of law.
COVID-19 and climate change
Mr. Chambas said COVID-19 is only amplifying these conflict drivers, with grave implications for peace and security. Its disproportionate effect on women and girls has placed them at increased risk of femicide and sexual violence.
The #COVID19 pandemic is amplifying and exacerbating pre-existing conflict drivers with grave implications for peace and security in West Africa and the Sahel," Special Representative Mohamed Ibn Chambas said when he briefed the @UN Security Council today. https://t.co/fxR45U2Nro pic.twitter.com/vuYMn8XDT3
— UN Political and Peacebuilding Affairs (@UNDPPA) July 9, 2020
Speaking to those vulnerabilities, Hindou Oumarou Ibrahim, Coordinator of the Association for Indigenous Women and Peoples of Chad, said COVID-19 is exacerbating the impact of climate change. People in her nomadic community depend on the environment to survive.
They used to follow the rainfall in the Central African Republic (CAR), but due to lockdowns brought on by the pandemic, they remain in their area – and cattle are dying. “When there is drought for cattle, there is food insecurity for the people,” she said.
Climate change in the Sahel has become “a nightmare” for millions. “Whether we have a lot of rain that floods crops, or drought, which shrinks resources, it ends in conflict among communities fighting for access to land or water,” she told the Council.
Lake Chad has shrunk by 90 per cent since 1960. Today, 40 million people now depend on these resources. “Let me tell you today: climate change is the reality of our community.” Across the region, people used to live in harmony. Today, they are killing each other. “Not for power – just for the water”.
(With input from the United Nations)