Natural toxins likely killed hundreds of Botswana elephants: government

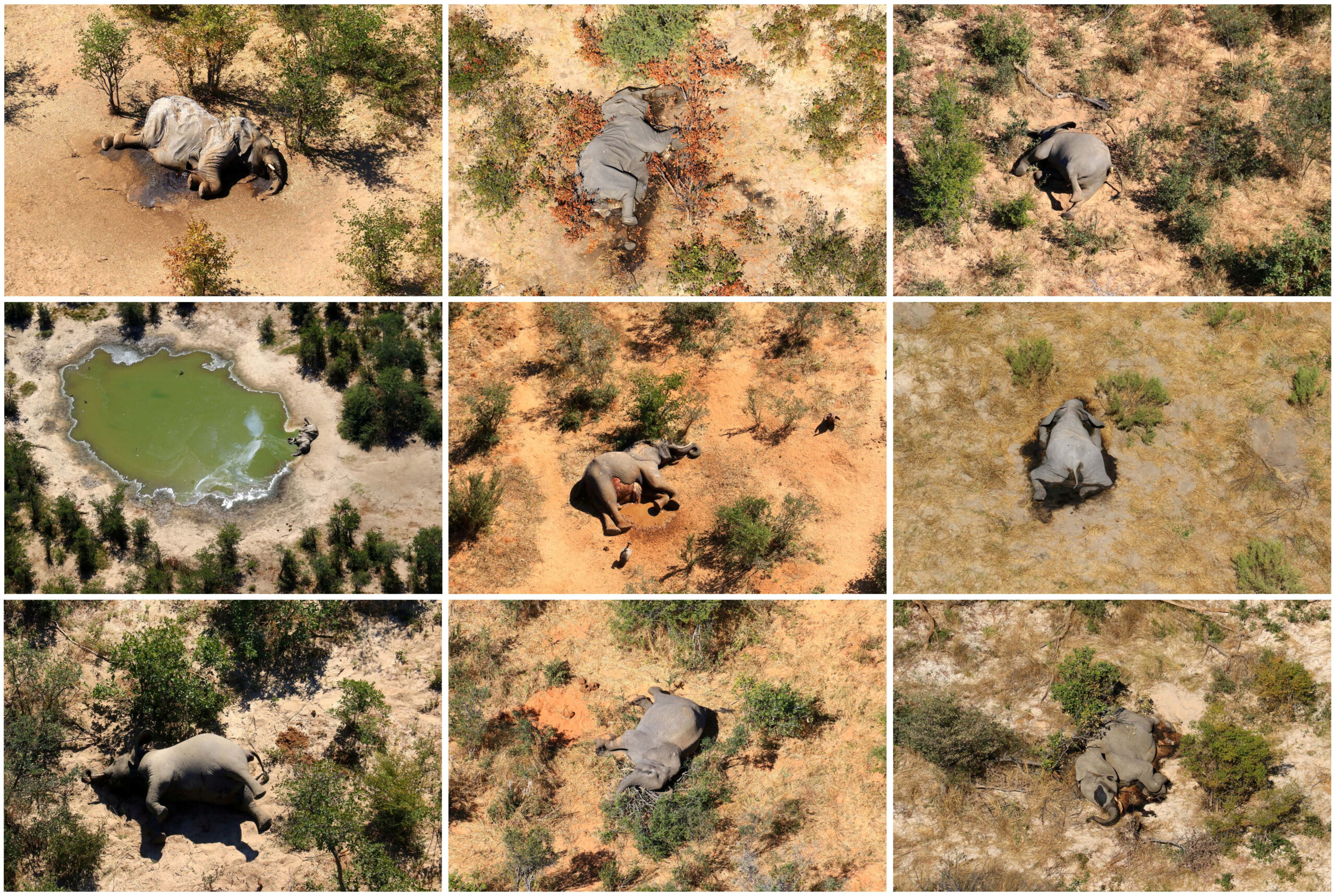
Hundreds of elephants that died mysteriously in Botswana’s famed Okavango Delta probably succumbed to natural toxins, the wildlife department said Friday.
The landlocked southern African country has the world’s largest elephant population, estimated to be around 130,000. Around 300 of them have been found dying since March.
Authorities have so far ruled out anthrax, as well as poaching, as the tusks were found intact.
Preliminary tests conducted in various countries far have not been fully conclusive and more are being carried out, Wildlife and Parks Department boss Cyril Taolo told AFP in a phone interview.
“But based on some of the preliminary results that we have received, we are looking at naturally-occurring toxins as the potential cause,” he said.
“To date we have not estabished the conclusion as to what is the cause of the mortality”.
He explained that some bacteria can naturally produce poison, particularly in stagnant water.
Government has so far established that 281 elephants died, although independent conservationists say more than 350.
The deaths were first flagged by a wildlife conservation charity, Elephants Without Borders (EWB), whose confidential report referring to the 356 dead elephants was leaked to the media early in July.
EWB suspected elephants had been dying in the area for about three months, and mortality was not restricted to age or gender.
Several live elephants appeared weak, lethargic and emaciated, with some showing signs of disorientation, difficulty in walking or limping, EWB said.
Tests are being conducted at specialist labs in South Africa, Canada, Zimbabwe and the US.