WHO experts propose additional experimental Ebola vaccine

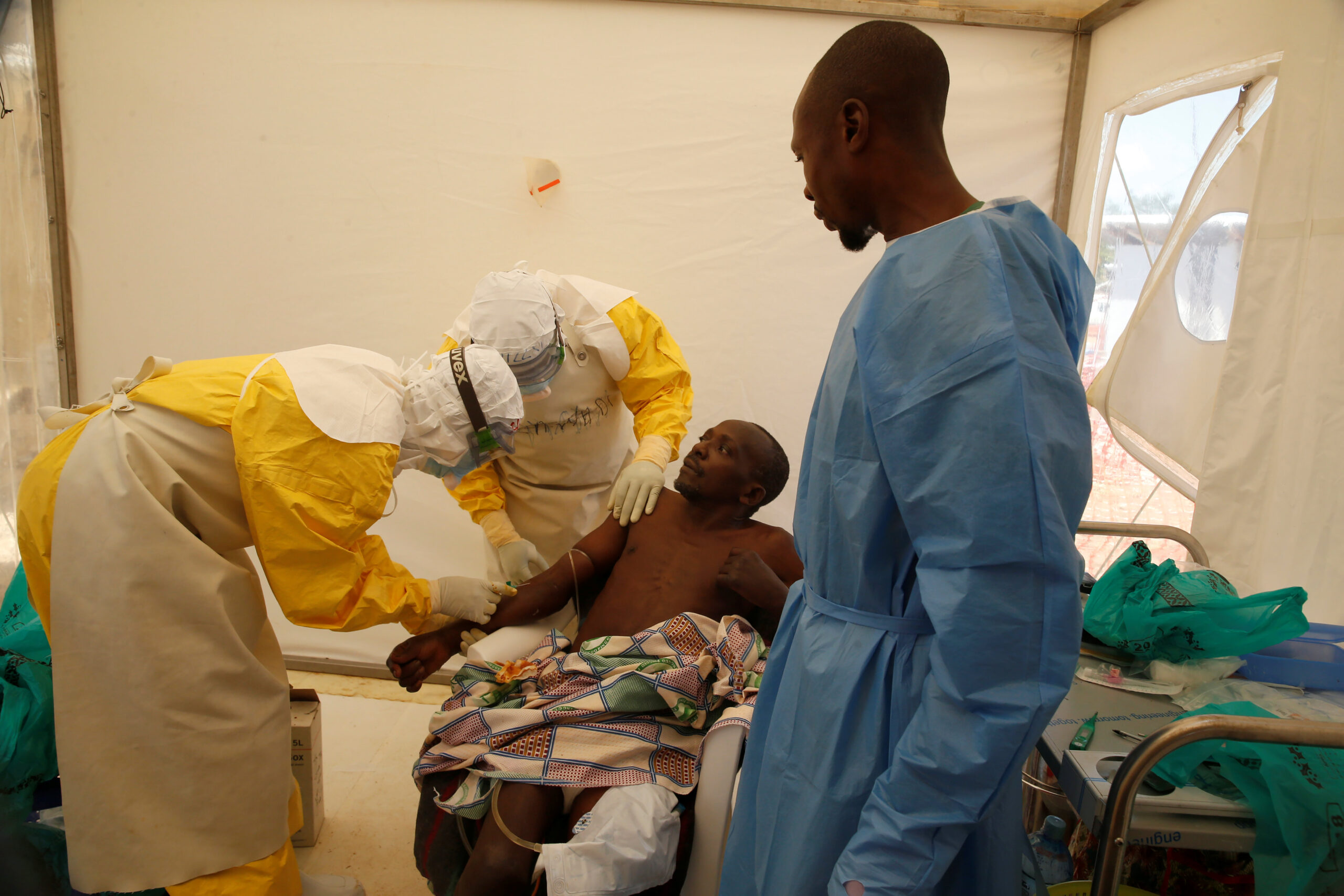
The World Health Organisation’s Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) has recommended the introduction of an additional experimental vaccine against Ebola, developed by Johnson & Johnson.
The WHO says the vaccine is being considered and a team is at an advanced stage towards the deployment and assessment of the vaccine.
The WHO also recommends offering an alternative vaccine, other than the existing one, to people at lower risk within affected health areas. Additionally, the WHO wants a redoubling of efforts to train nurses, doctors and medical students from Ebola-affected communities to work on vaccination teams.
The experts also proposed that people who could be part of tertiary chains of transmission be vaccinated. These people include those in villages and neighborhoods where cases have been reported within the past 21 days.
The WHO says increasing access to vaccination in the broader community may help improve community acceptance of the vaccine and other control measures.
The recommendations are part of efforts to address vaccination challenges in the ongoing Ebola outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
They were made following a report by the WHO that the numbers of Ebola cases are on the rise despite the use of a highly effective vaccine.
More than 111,000 people have been vaccinated in the Democratic Republic of Congo since the outbreak was declared in August 2018.
The WHO says this is, in part, due to repeated incidents of violence which affect the ability of response teams to immediately identify and create vaccination rings around all people at risk of contracting Ebola.
The number of people known to have contracted the disease has exceeded 1,000. The figure, confirmed by the country’s health ministry, makes the outbreak the second largest ever recorded.